1. Purchase Order (PO)
A document issued by a buyer to a supplier, confirming an order.
Example: “We sent a purchase order for 1,000 units to the supplier.”
2. Request for Proposal (RFP)
A document inviting suppliers to bid on supplying goods or services.
Example: “Our RFP generated several competitive bids from vendors.”
3. Request for Quotation (RFQ)
A request asking suppliers to provide a price for specific goods or services.
Example: “We issued an RFQ for office supplies to find the best price.”
4. Invoice
A bill sent by the supplier to the buyer for goods or services delivered.
Example: “The invoice for the shipment is due in 30 days.”
5. Terms of Payment
The agreed payment conditions between buyer and supplier.
Example: “Our terms of payment are net 30, meaning payment is due within 30 days.”
6. Supplier Evaluation
Assessing suppliers based on criteria like price, quality, and reliability.
Example: “We conduct supplier evaluations annually to ensure quality.”
7. Procurement
The process of acquiring goods and services from suppliers.
Example: “Effective procurement strategies help us manage costs.”
8. Lead Time
The time it takes for an order to be fulfilled from start to finish.
Example: “The lead time for new equipment is four weeks.”
9. Reorder Point
The stock level that triggers a new order to prevent shortages.
Example: “We set the reorder point for parts at 100 units.”
10. Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ)
The smallest quantity a supplier is willing to sell.
Example: “The supplier’s MOQ for widgets is 500 units.”
11. Safety Stock
Extra inventory kept to avoid stockouts.
Example: “We maintain safety stock to handle unexpected demand.”
12. Stock Keeping Unit (SKU)
A unique identifier for each product in inventory.
Example: “Every SKU has specific details, like color and size.”
13. Just-in-Time (JIT)
A strategy to reduce inventory by receiving goods only when needed.
Example: “JIT reduces storage costs but requires accurate demand forecasting.”
14. Inventory Turnover
The rate at which inventory is sold and replaced over time.
Example: “High inventory turnover indicates strong product demand.”
15. Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)
The optimal order size to minimize holding and ordering costs.
Example: “Using EOQ helps us avoid excess inventory.”
16. Dead Stock
Inventory that cannot be sold.
Example: “We have dead stock from last year’s unsold seasonal items.”
17. Cycle Counting
Regular counting of portions of inventory to ensure accuracy.
Example: “Cycle counting allows us to maintain inventory accuracy.”
18. ABC Analysis
A method of categorizing inventory by importance, based on value and usage.
Example: “In ABC analysis, ‘A’ items are high-value and low-quantity.”
19. Backorder
An order for an item that is temporarily out of stock.
Example: “The part is on backorder and will arrive next month.”
20. Inventory Shrinkage
The loss of inventory due to factors like theft or damage.
Example: “Inventory shrinkage affects profitability and must be minimized.”
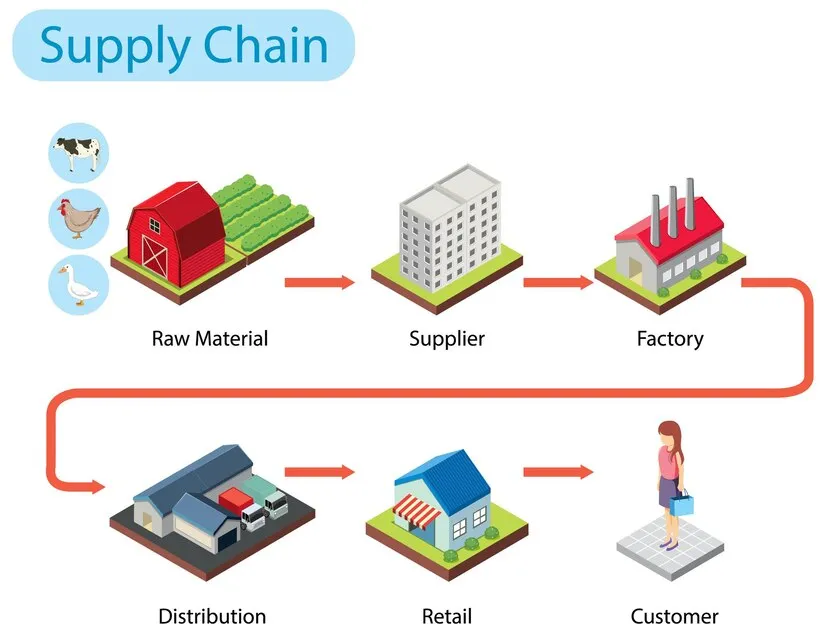
21. Supply Chain
The entire network involved in producing and delivering a product.
Example: “Our supply chain includes raw material suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors.”
22. Demand Forecasting
Predicting future demand for products.
Example: “Accurate demand forecasting prevents overproduction.”
23. Supply Chain Management (SCM)
Managing the flow of goods and services across the supply chain.
Example: “Effective SCM improves efficiency and reduces costs.”
24. Supplier Relationship Management (SRM)
Building and maintaining positive relationships with suppliers.
Example: “Our SRM program helps us negotiate better contract terms.”
25. Logistics
Coordinating the movement and storage of goods from origin to destination.
Example: “Our logistics team ensures timely delivery of products.”
26. Sourcing
Finding and selecting suppliers for goods and services.
Example: “We’re sourcing new vendors for our raw materials.”
27. Capacity Planning
Determining the production capacity needed to meet demand.
Example: “Capacity planning ensures we can meet seasonal spikes.”
28. Distribution
The process of delivering products to end users.
Example: “Our distribution network includes local and international partners.”
29. Supply Chain Visibility
The ability to track products throughout the supply chain.
Example: “Improved visibility helps us manage delays effectively.”
30. Outsourcing
Contracting work to external suppliers rather than handling it in-house.
Example: “We outsource some manufacturing to reduce costs.”

31. Freight
Goods transported by truck, ship, plane, or rail.
Example: “We chose air freight for a faster delivery.”
32. Third-Party Logistics (3PL)
Using external companies to handle logistics and distribution.
Example: “A 3PL provider manages our warehousing and shipping.”
33. Carrier
A company that transports goods.
Example: “Our carrier offers competitive rates for bulk shipments.”
34. Bill of Lading (BOL)
A document listing goods in transit, serving as a receipt.
Example: “The BOL details the items and quantities shipped.”
35. Freight Forwarder
A company that arranges the shipping of goods on behalf of others.
Example: “Our freight forwarder coordinates international shipments.”
36. FOB (Free on Board)
A shipping term indicating when responsibility for goods transfers to the buyer.
Example: “FOB origin means the buyer is responsible once goods leave the supplier.”
37. Cross-Docking
Transferring products directly from inbound to outbound trucks without storage.
Example: “Cross-docking reduces storage needs and speeds up delivery.”
38. Shipping Manifest
A document detailing the contents of a shipment.
Example: “The manifest includes item descriptions and quantities.”
39. Reverse Logistics
The process of returning goods from customers to suppliers.
Example: “Reverse logistics handles product returns and recycling.”
40. Freight Consolidation
Combining smaller shipments to save on shipping costs.
Example: “Freight consolidation helps reduce shipping expenses.”
41. Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
The complete cost of acquiring, operating, and maintaining an asset.
Example: “We evaluate TCO when selecting equipment to understand long-term costs.”
42. Fixed Price Contract
A contract where the payment amount does not change regardless of expenses.
Example: “The supplier agreed to a fixed-price contract for the project.”
43. Cost-Plus Contract
A contract where the buyer pays for expenses plus a profit margin.
Example: “The cost-plus contract covers raw material costs and labor.”
44. Break-Even Analysis
Determining the sales level required to cover costs.
Example: “The break-even analysis showed we need to sell 500 units.”
45. Benchmarking
Comparing processes or performance metrics to industry standards.
Example: “We benchmark our logistics costs against competitors.”
46. Negotiation
The process of reaching an agreement on terms between buyer and supplier.
Example: “We negotiated a volume discount for large orders.”
47. Value Analysis
Reviewing product design to reduce costs without affecting quality.
Example: “Value analysis helped us cut material costs by 15%.”
48. Price Variance
The difference between the expected and actual price of goods or services.
Example: “Price variance occurred due to unexpected material cost increases.”
49. Supplier Development
Assisting suppliers in improving performance to meet business needs.
Example: “Our supplier development program includes regular training sessions.”
50. Bulk Purchasing
Buying large quantities to secure a discount.
Example: “Bulk purchasing reduced our per-unit cost by 10%.”
51. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Metrics used to measure supply chain performance.
Example: “KPIs include order accuracy and delivery times.”
52. Order Fill Rate
The percentage of customer orders fulfilled without delay.
Example: “Our fill rate improved after streamlining warehouse processes.”
53. On-Time Delivery (OTD)
The rate of orders delivered on or before the due date.
Example: “Our OTD score is critical for customer satisfaction.”
54. Perfect Order Rate
The percentage of orders delivered without issues.
Example: “A high perfect order rate reflects efficient operations.”
55. Supplier Lead Time Variability
Variations in supplier lead times.
Example: “We monitor lead time variability to adjust order schedules.”
56. Freight Cost per Unit
Shipping cost per product unit.
Example: “Reducing freight cost per unit can improve profit margins.”
57. Inventory Accuracy
The precision of inventory records compared to actual stock.
Example: “Cycle counting improves inventory accuracy.”
58. Days Inventory Outstanding (DIO)
The average number of days inventory is held before sale.
Example: “Lower DIO means faster turnover of inventory.”
59. Order Cycle Time
The time from order placement to fulfillment.
Example: “Reducing cycle time improves customer satisfaction.”
60. Stockout Rate
The frequency at which inventory runs out.
Example: “Minimizing stockout rate ensures customer needs are met.”

61. Demand Planning
Forecasting demand to optimize supply chain operations.
Example: “Accurate demand planning prevents overstocking and shortages.”
62. Material Requirements Planning (MRP)
A system for managing inventory, production, and scheduling.
Example: “MRP helps us plan raw material orders efficiently.”
63. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
Software for integrating business processes and information.
Example: “ERP allows us to manage purchasing, inventory, and sales in one system.”
64. Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI)
An arrangement where the supplier manages stock levels for the buyer.
Example: “With VMI, the supplier refills inventory as needed.”
65. Forecast Accuracy
The precision of demand forecasts versus actual sales.
Example: “Improving forecast accuracy helps reduce stockouts.”
66. Risk Mitigation
Actions taken to reduce supply chain risks.
Example: “We have a risk mitigation strategy to handle supplier disruptions.”
67. Supply Chain Resilience
The ability of a supply chain to adapt to changes or disruptions.
Example: “Our resilient supply chain managed the unexpected demand spike.”
68. Dual Sourcing
Using two suppliers for a critical item to reduce risk.
Example: “Dual sourcing secures our supply chain in case of disruption.”
69. Cost Reduction
Efforts to lower purchasing and operational expenses.
Example: “Negotiating bulk discounts contributes to cost reduction.”
70. Sustainable Sourcing
Purchasing materials in an environmentally responsible way.
Example: “We prioritize sustainable sourcing for our raw materials.”
71. Risk Assessment
The process of identifying and evaluating potential risks in the supply chain.
Example: “A risk assessment revealed vulnerabilities in our supplier network.”
72. Compliance
Adhering to legal, regulatory, and industry standards in operations.
Example: “Our suppliers must comply with environmental regulations.”
73. Supplier Compliance
Ensuring that suppliers meet specific standards and regulations.
Example: “We conduct regular audits to verify supplier compliance.”
74. Customs Compliance
Adhering to government regulations on importing and exporting goods.
Example: “Customs compliance is essential for avoiding delays in shipments.”
75. Regulatory Risk
The risk of non-compliance with government regulations impacting the supply chain.
Example: “New trade policies have increased our regulatory risk.”
76. Hazardous Materials (HazMat)
Items that require special handling due to safety concerns.
Example: “We follow strict guidelines for transporting HazMat goods.”
77. Import Tariff
A tax imposed on imported goods.
Example: “The new import tariffs have increased our costs on foreign parts.”
78. Trade Compliance
Adhering to rules and laws governing international trade.
Example: “Our trade compliance team ensures that all exports are documented correctly.”
79. Anti-Bribery Policy
A policy prohibiting bribery and corruption in business transactions.
Example: “Our anti-bribery policy applies to all vendor interactions.”
80. Third-Party Risk
Risks associated with outsourcing parts of the supply chain to other companies.
Example: “We assess third-party risk before contracting new suppliers.”
Sign up and experience our high-quality English courses firsthand.
Take your career to the Next Level by Mastering Business English

















